By providing technical leadership for the design, development, and roll-out of Tanzania’s first-ever HIV-sensitive National Integrated Case Management System (NICMS) for OVC, Bantwana has enhanced Tanzania’s social welfare workforce and helped PEPFAR OVC Implementing Partners link more than 700,000 orphans and vulnerable children to essential services. The NICMS is the flagship achievement and lasting legacy of the USAID/PEPFAR-funded Community Health and Social Welfare Systems Strengthening Program (CHSSP) led by JSI Research & Training Institute, Inc. (JSI).
In Tanzania, HIV is among the leading causes of death, particularly among young people. According to UNAIDS, the country has approximately 1.64 million people living with HIV. Of those, only 18% of children living with HIV are virally suppressed, as compared to 84% of adults. (Tanzania HIV/AIDS Indicator Survey 2016-2017) Finding undiagnosed children and adolescents, linking them to care and treatment, and helping them to achieve and maintain viral suppression requires coordinated efforts between clinical health workers and community based social welfare providers. Tanzania lacks the necessary human resources for social welfare needed to control the HIV epidemic, with the biggest gaps at the community level.
Responding to the Need
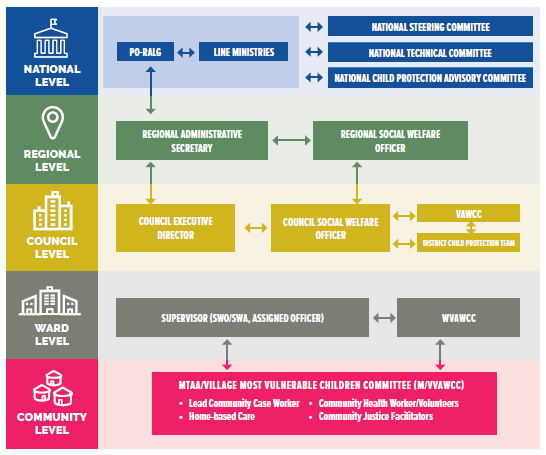
Strategically positioned at the nexus of collaboration between community and facility implementing partners, the National Integrated Case Management System strengthens the social welfare workforce and connects and coordinates all service providers — governmental and non-governmental; local, district, regional, and national — working with OVC across Tanzania’s health, protection, and social welfare sectors. (Watch this short overview video about the NICMS.)
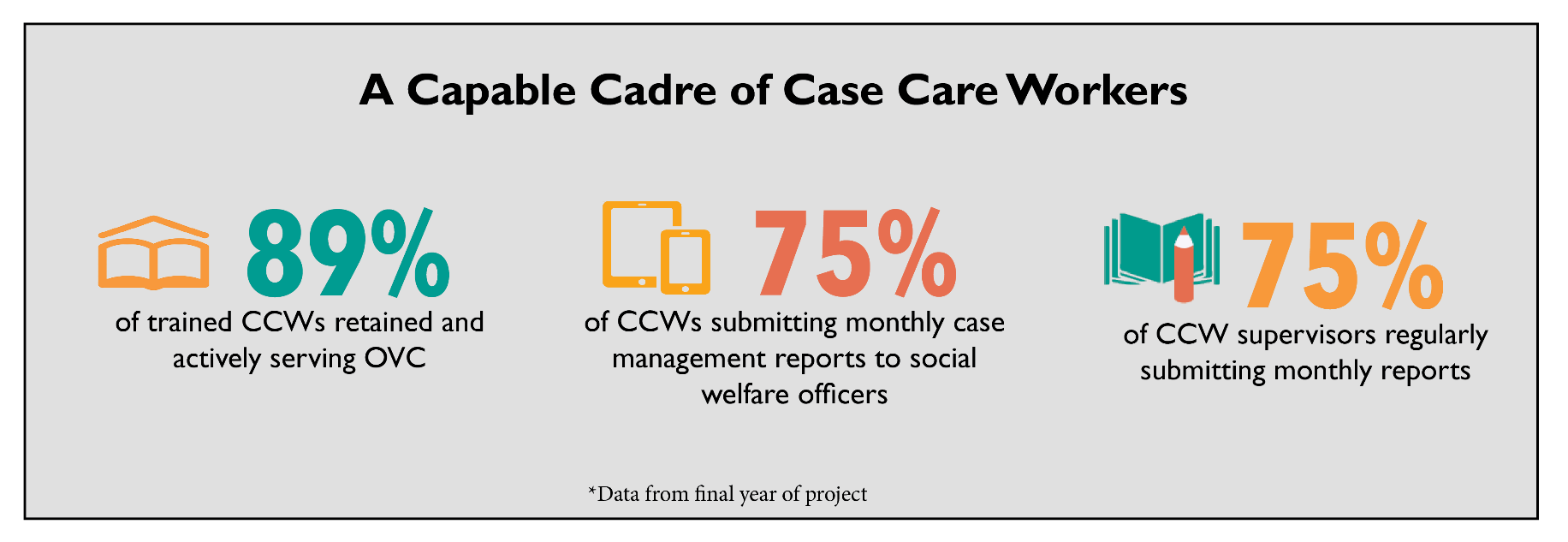
Bantwana’s expert technical assistance and support ensured a harmonized approach to OVC case management that actively facilitates referrals across the HIV care continuum to link at risk children, adolescents, and their families to the full range of HIV and wrap around social welfare and protection/GBV services. The NICMS strengthened human resources for social welfare and HIV epidemic control where they are most needed – at the grassroots level. Capacity-development inputs built skills, retention, and meaningful supportive supervision among a nation-wide cadre of community case workers. The NICMS will continue beyond CHSSP as a legacy for creating a stronger social welfare workforce and integrating community structures that can identify at risk children and adolescents and get them tested, linked to care, retained on treatment, and virally suppressed.
See the NICMS in action!
Local Ownership in Action
Now, after the NICMS was developed, approved by the government, and scaled up with CHSSP support, it is clear that Tanzania has taken full “ownership” of the system. NICMS has been nationalized, to ensure all implementing partners working with vulnerable populations and in social services use its data collection and reporting tools. The government has also mandated that all councils budget and plan for NICMS implementation.
This diagram highlights the “national” and “integrated” aspects of the National Integrated Case Management System.
A district capacity assessment conducted in 2020 showed that councils implementing NICMS perform better, particularly in planning, coordination, budgeting, and quality of case management.
Results such as the above were possible and are now sustainable, in large part, because of the following:
- Strong ownership of the NICMS by the Government of Tanzania at the National and District levels
- A winning combination of expert OVC case management technical assistance from Bantwana, strong project leadership from JSI, and cutting-edge district level capacity development support from both Bantwana and JSI
- Development, testing, and dissemination of a core national training package for CCWs, including a set of instructional videos in Kiswahili to improve the quality of case management documentation
- Development of a Comprehensive Council Operational Planning for Social Welfare (CCSWOP) that provides guidelines for multi-sectoral planning, budgeting, and reporting of social welfare services at the Council level; and
- The revitalization of the Violence against Women and Children Committees, whose members now have the skills and knowhow to refer victims to post-violence care services, including PEP; post-trauma counseling; HIV testing, care, and treatment; and legal services.
Want to learn more about the NICMS and Bantwana’s contributions to CHSSP? Watch these short videos:







